Define Listening Skills and its Types | What are the 8 barriers to listening?
Listening skills is one of the key attributes for every professional. In personal and professional life, we are always listening to something. We may be listening to a person from a different culture, speaking a different language or someone who is an expert in his/her field. Listening skills help you understand and relate to the other person better and also help you retain more information.
What are Listening Skills?
The most important part of oral communication is listening. When we listen we engage our minds actively. There is a difference between listening and hearing.
Listening is a conscious activity of the mind whereas hearing is an unconscious activity. Listening is neglected in our schools and colleges.
This is one of the skills, which should be taken seriously. It is considered a significant part of one’s communication skills.
In order to understand any language, one has to be a keen listener. As soon as a child comes into this world he starts “listening”. He develops listening skills in his mother tongue and on the basis of a listening model speech he develops patterns for speech production.
Reading and writing come later in the hierarchy of developing language skills. The language teachers suggest the development of listening skills at an early stage.
Children can easily learn the actual pronunciation of English words that will enable them to involve in communication with better use of the target language.
Listening Definition
According to Dumont and Lennon, “Listening is the complex and selective process of receiving, focusing, deciphering, accepting and storing.”
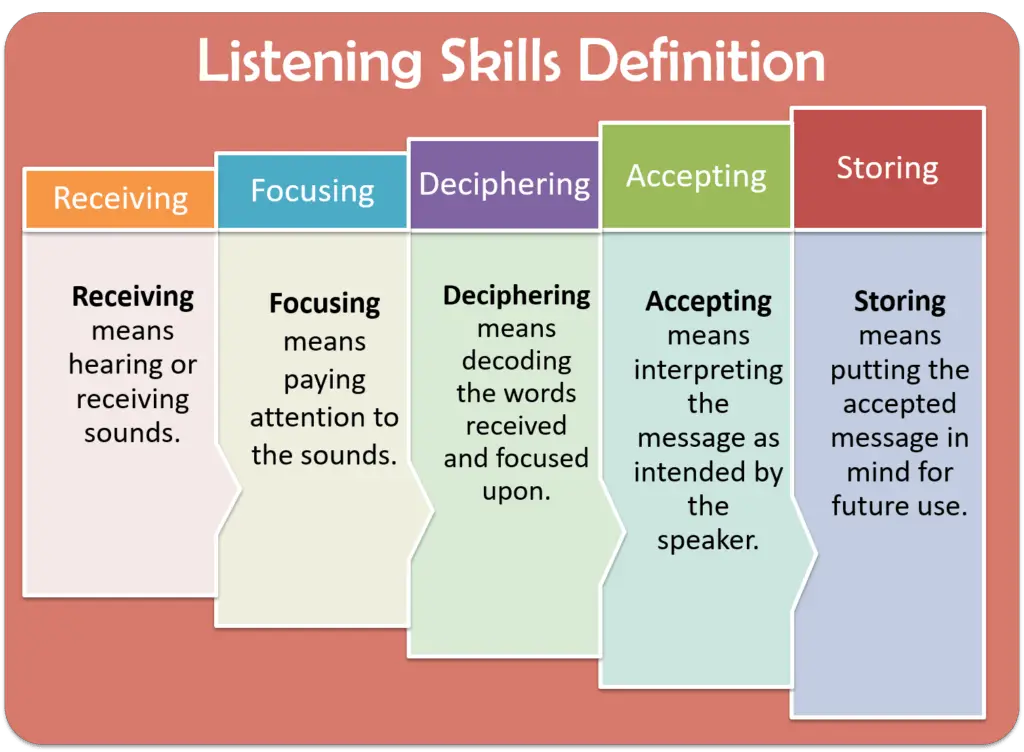
Listening takes place only when all the processes are present.
Receiving: The first process is receiving sounds. It means hearing or receiving sounds.
Focusing means paying attention to the sounds.
Deciphering means decoding the words received and focused upon.
Accepting means interpreting the message as intended by the speaker.
Storing means putting the accepted message in mind for future use.
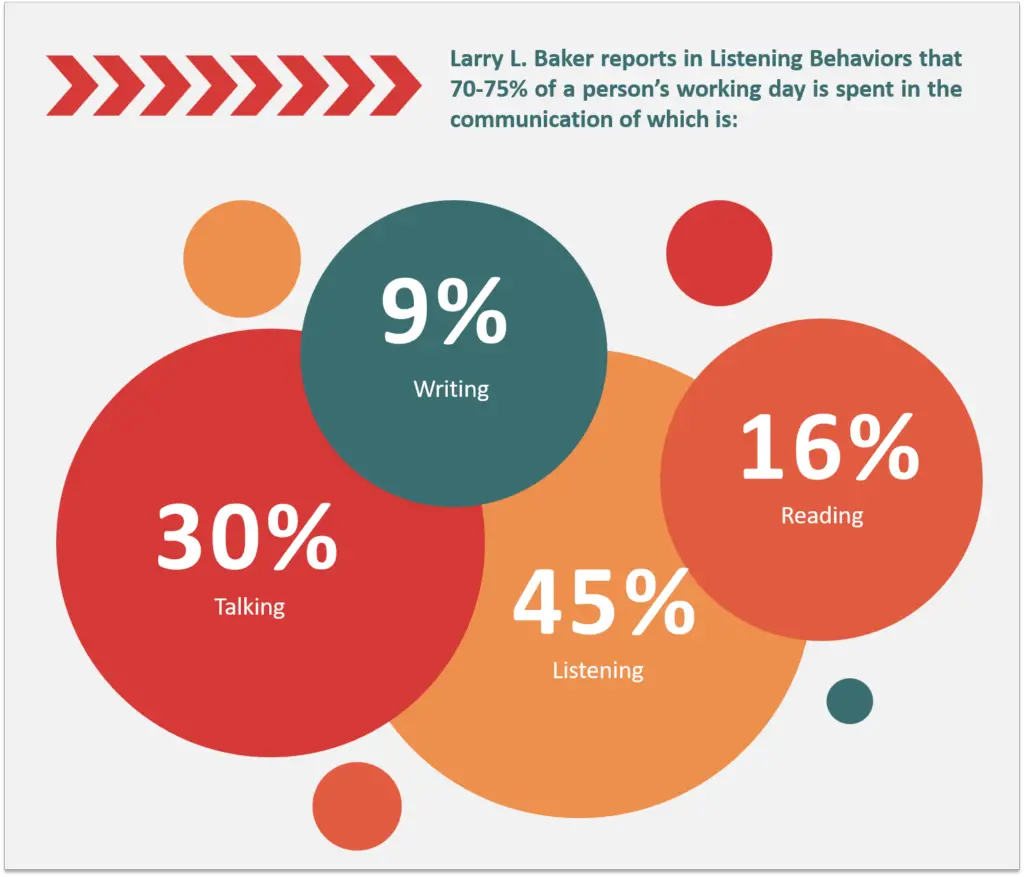
Larry L. Baker reports in Listening Behaviours that 70-75% of a person’s working day is spent in the communication of which:
- 45% is listening
- 30% is talking
- 16% is reading and
- 09% is writing
Purpose of Listening
Listening is an important activity of paying attention and trying to get meaning from something we hear. To listen successfully we need to be able to work out what speakers mean when they use particular words on particular occasions and not simply to understand words themselves.
According to Kathleen Gulvin, there are five main reasons for listening:
They are:
- To engage in social rituals
- To exchange information
- To exert control
- To share feelings.
- To enjoy yourself.
Why Listening Skills are necessary?
Effective listening requires a conscious effort and a willing mind. Generally, there are four reasons.
To Gain New Information & Ideas
Most of the learning comes through listening. Effective listeners welcome new information and ideas. New ideas are received daily by oral medium. You get knowledge by listening to the lectures in class. Companies that listen effectively stay informed and up to date.
To Test Evidence
When a speaker talks, he actually presents the message based on facts and opinions. Good listeners test those facts and opinions and then question the speaker to know the truth. They try to uncover the speaker’s point of view and credibility.
To Be Inspired
Sometimes people listen to get inspiration. By listening attentively, they get inspired and ready to take action.
To Improve Your Own Communication
Listening also improves your own communication. Role models are helpful to young people entering the business world. They can learn communication skills by hearing and observing the speeches of the role models.
Types of Listening
There are two types of listeners i.e. active listeners and passive listeners which formulate the following two terms.
- Active listening
- Passive Listening
Active Listening
Active listening is the process of understanding fully what the speaker has said both in content and in feeling. In the active listening, you are both mentally and physically prepared.
Your body language indicates your interest in the message. The function and purpose of active listening are to check on the accuracy of understanding.
Three simple techniques that are useful in the process of active listening as follows:-
- Restate the speaker’s meaning in your own words
- Express the understanding of the speaker’s feelings.
- Ask questions to ensure further understanding of the speaker’s thoughts and feelings.
Passive Listening
Listening without talking and without directing the speaker in any non-verbal way is known as passive listening. In passive listening, you are physically present but mentally absent.
Sometimes you are not willing to receive an oral message but you are forced to do so. So you feel boredom and become a passive listener. As a result, you fail to recall the contents of the message.
What are the 8 barriers to listening?
1 – Prejudgment
Prejudgment is one of the most common problems to listening. It can be difficult to overcome because it is an automatic process. Listeners who jump to conclusions close their minds to additional information.
2 – External Distraction
Not only the verbal messages but also the non-verbal cues affect listening. Actually, the entire physical environment affects listening. Among the negative factors are noisy fans, poor or glaring lights, extreme weather, sloppy dressing, and so on.
3 – Prejudice
All of you have personal opinions, attitudes, or beliefs about certain things. When you like someone, you pay attention to him. If you have a certain prejudice against the speaker, you will not like to listen to the speaker.
4 – Self-Centeredness
Self-centeredness causes some people to take control of conversation rather than listen to what’s being said. Self-centered listeners shift their attention from the speaker to themselves.
For example, if a speaker mentions a problem (perhaps a manager is trying to deal with the conflict between team members), self-centered listeners relate their own problems with the conflict.
5 – Selective Listening
Another problem is selective listening. When you listen selectively, you will listen what is of your interest.
6 – Monotone
A monotone can readily put listeners to sleep or cause them to loose interest. They become bored and critical in such situations.
7 – Thinking Speed
The average thinking capacity of a person is up to 800 words per minutes while the speaker utters 80 to 160 per minute. This difference sometimes makes listeners deviate from the speaker’s words and they shift to something else.
8 – Semantic Barrier
The meaning of words also creates a problem in listening, as the meaning of words varies from person to person, influenced by feelings, attitudes, prejudices, and biases. Sometimes the way a speaker utters a word annoys us, thus our listening is impaired.

Techniques for Effective Listening
- Focus your attention
- Listen to understand not refute
- Fight Distractions
- Don’t Interrupt
- Maintain Eye Contact
- Be Positive
- Ask Questions
- Take Notes
- Provide Feedback
- Summarize & Evaluate
Results of Good Listening
The following benefits will occur as a result of good listening.
- It builds relationships, encourages understanding of the other person’s feelings and point of view
- It adds information, stimulates new ideas and solve problems
- It helps to improve communication
- It helps to overcome obstacles in the way of listening
- It indicates feedback to the speaker to show that the listeners are interested
- It offers the opportunity to use the speaker’s tone of voice, to interpret the message
- It assists the speaker especially in the interview to talk out a problem
Some Activities
Activity 1
After listening to the weather forecast in the news transmission answer the following questions:
- What would be the weather condition in south Punjab during the next 24 hours?
- Describe the places where rain is expected.
- Give an overall forecast of weather in northern areas.
Activity II
After listening to the speech of the Quaid-e-Azam, answer the following questions:
- Sump up the message of the Quaid-e-Azam?
- In his address, what is advised to the students by the Quaid-e-Azam?
- Guess the occasion at which the Quaid-e-Azam delivered his speech.
Activity III
Reading aloud the following extract, the teacher may ask the questions given in the end:
“Man is a work of art. In his making the stress has been laid neither on the mechanical nor on the moral but on the imaginative. Man’s “well-wishers” try to screen this truth, but the truth blazes up and burns the screen. At last in dismay, the school master and man’s well-wishers try to bring about terms of peace between morality and fiction. But the two meet only to hack at each other and the pile of waste mounts up in heaps.
Questions
- Give it a title.
- Fill in the blanks:
- Man is a _______________.
- Man’s ______________try to screen this truth.
- The pile of waste ___________.
- Correct the false sentences if any:
- In man’s making the stress has been laid on the imaginative
- Man is a work of science
- Man’s well-wishers try to improve this truth
- The passage is about nature.
- A suitable title for the passage is: “The Animal World”
Further Reading







learning english well