How do you describe adjectives? 13 Types of Adjectives with Examples
The words which tell something mere or describe or qualify a noun or a pronoun are called “the adjectives”.
They may tell the quality or quantity of the noun or pronoun for which they are used. It is used before a noun and after linking verb.
For example, beautiful, tall, wise, poor, fine, large etc. They all are showing some quality or make prominent of something or some person.
Degrees of Adjectives Rules
There are three degrees of adjectives.
- Positive Degree
- Comparative Degree
- Superlative Degree
Rule – A
To make degree of adjective we use ‘er’ for second and ‘est’ for third degree.
Examples
| 1st Degree | 2nd Degree | 3rd Degree |
| Black | Blacker | Blackest |
| Hard | Harder | Hardest |
| Slow | Slower | Slowest |
| Big | Bigger | Biggest |
Rule – B
The rule is that when the word is a pronoun or comprised of two or more syllables, we use more for the second degree and most for the third degree.
| 1st Degree | 2nd Degree | 3rd Degree |
| Angry | More angry | Most angry |
| Beautiful | More beautiful | Most beautiful |
| Charming | More charming | Most charming |
Rule – C
The adjectives which end on y, ow, er, and comprise upon two-syllable, for them, we usually add ‘er’, ‘est’.
| 1st Degree | 2nd Degree | 3rd Degree |
| Simple | Simpler | Simplest |
| Noble | Nobler | Noblest |
| Happy | Happier | Happiest |
Rule – D
With following syllable adjectives, we use ‘er/est’ or ‘more/most’
| 1st Degree | 2nd Degree | 3rd Degree |
| Common | Commoner | Commonest |
| Clever | Cleverer | Cleverest |
| Handsome | Handsomer | Handsomest |
With the above adjectives, we can use ‘more’ in second degree and ‘most’ in third degree.
Rule – E
Irregular comparisons of adjectives
| 1st Degree | 2nd Degree | 3rd Degree |
| Far | Father | Farthest |
| Little | Less | Least |
| Late | Latter | Last |
| Fore | Former | Foremost |
| Old | Older | Oldest |
Rule – F
Do not use ‘more’ when the adjective is present with ‘er’.
Examples
- He is more stronger than is brother. (Incorrect)
- He is stronger than his brother. (Correct)
Rule – G
For comparison, use ‘than’ instead of ‘from’.
Example
- He is older from his friend. (Incorrect)
- He is older than his friend. (Correct)
Rule – H
With the adjectives, senior, junior, inferior, superior, prefer, or prior, we use ‘to’.
- He is more intelligent than I. (Incorrect)
- He is intelligent to me. (Correct)
- He prefers juice than tea. (Incorrect)
- He prefers juice to tea. (Correct)
- His shirt is costly than mine. (Incorrect)
- His shirt is costly to mine. (Correct)
Rule – I
In the comparative degree of adjectives, sometimes we use ‘the’ in order to specify something.
- Salma is clever of the two sisters. (Incorrect)
- Salma is the clever of the two sisters. (Correct)
Rule – J
‘Some’ is used in affirmative while ‘any’ is used in negative sentences.
- Bring me some water to drink.
- I did not give him any money.
‘Much’ speaks quantity while ‘many’ denotes number.
- There is much water in the jug.
- There are many students in the classroom.
Pair of words in the use of adjectives
Besides (by the side) : Beside (in addition, further, more)
- He is sitting besides me. (Incorrect)
- He is sitting beside me. (Correct)
- Little means hardly, a little means some and the little means something already present.
- A little money is better than none.
- I am sorry to find that I have little money.
Always use ‘to’ after elder or eldest.
- I am elder to my sister by two years.
Types of Adjectives
Following are different types of adjectives.
- Possessive Adjective
- Absolute Adjective
- Adjective of Quality
- Adjective of Quantity
- Adjective of Number
- Adjective of Shape
- Adjective of Color
- Adjective of Origin
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Indefinite Adjectives
- Interrogative Adjective
- Adjective of Position
- Distributive Adjective
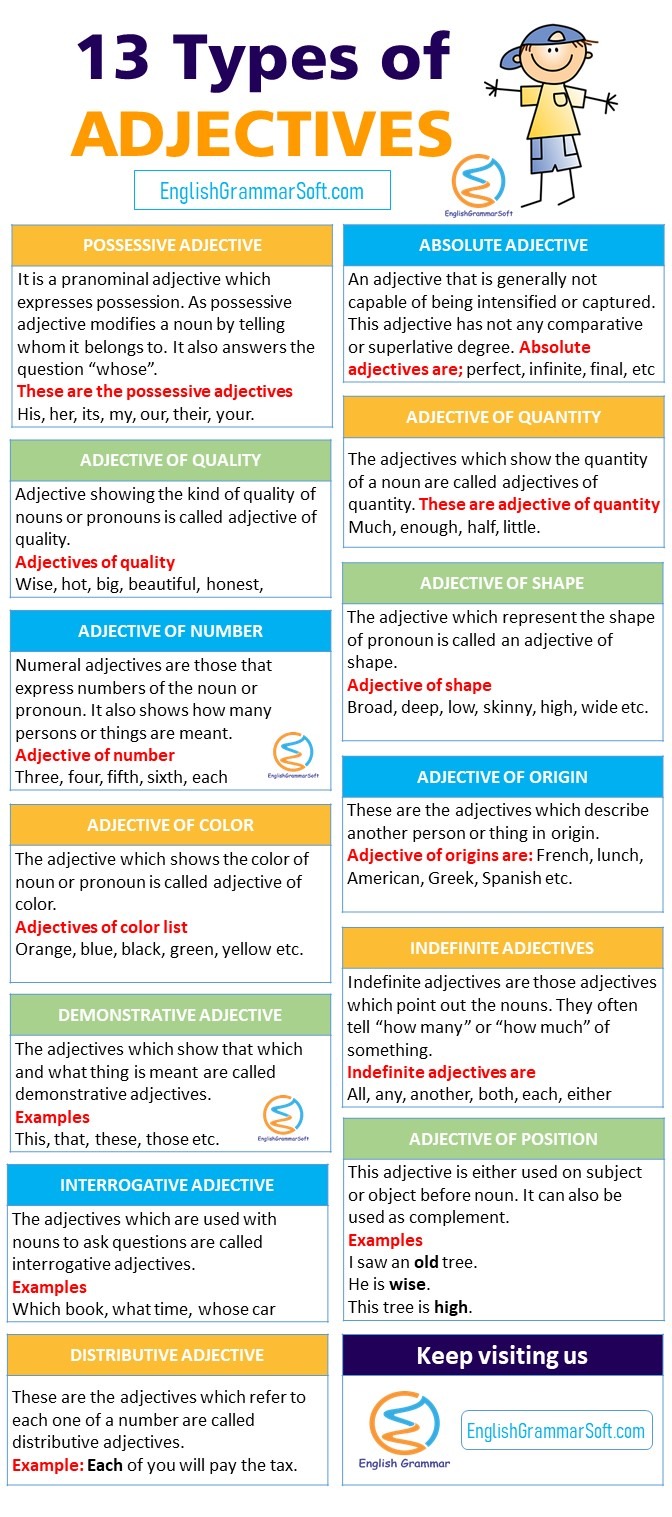
1 – Possessive Adjective
It is a prenominal adjective that expresses possession. A possessive adjective modifies a noun by telling whom it belongs to. It also answers the question “whose”.
These are the possessive adjectives
His, her, its, my, our, their, your
Examples
Use of possessive adjective in sentences
- You can share my room.
- This is his room.
- Have you seen their office?
- They are our enemies.
2 – Absolute Adjective
An adjective that is generally not capable of being intensified or captured. This adjective has not any comparative or superlative degree.
Absolute adjective list
- Perfect
- infinite
- final
- fatal
- eternal
- equal
- dead
- probably
- unique
- unanimous
- total
- supreme etc.
3 – Adjective of Quality
Adjective showing the kind of quality of nouns or pronouns is called adjective of quality.
Adjective of quality list
- Wise
- hot
- big
- beautiful
- honest
- red
- rich
- poor
- tall
- small
- fresh
- active.
Examples
Use of adjective of quality in sentences
- Ahmad is an honest boy.
- This rose is very beautiful.
- Jimmy is a brave boy.
- The color of his shirt is red.
- Tom is a wise man.
4 – Adjective of Quantity
The adjectives which show the quantity of a noun are called adjectives of quantity.
These are adjective of quantity
Much, enough, half, little.
Example Sentences
- He has much money.
- A lot of books are present in the library.
- A little milk is in the jug.
- Please give me some milk.
- He gave me a little doll.
5 – Adjective of Number
Numeral adjectives are those that express numbers of the noun or pronoun. It also shows how many persons or things are meant.
Adjective of number list
- Three
- four
- fifth
- sixth
- each
- any
- few
- many
Examples
- A thousand pounds.
- Akbar has one book, but Nadia has two books.
- I have many cars.
- Some questions are too difficult
- All the teachers are present.
Sometimes adjectives of number are not precise. For example, a few days, many days.
6 – Adjective of Shape
The adjective which represent the shape of pronoun is called an adjective of shape.
Adjective of shape list
- Broad
- deep
- low
- skinny
- high
- round
- steep
- flat
- curved
- wide etc.
Examples
- The river is not deep enough.
- This wall is flat.
- This table has round shape.
- There is narrow space in this room.
- This iron rod has curved shape.
7 – Adjective of Color
The adjective which shows the color of noun or pronoun is called adjective of color.
Adjectives of color list
- Orange
- blue
- black
- green
- yellow
- purple, etc.
Examples
- This shirt is of white color.
- The color of my shoes is black.
- He is sitting on yellow color desk.
- The walls of my room are purple.
- The color my bicycle is blue.
8 – Adjective of Origin
These are the adjectives which describe another person or thing in origin.
- French
- lunch
- American
- Greek
- Spanish etc.
Examples
Use of adjective of origin in sentences
- I obtained this pen from my Greek friend.
- One of my French friend will come to meet me this Friday.
9 – Demonstrative Adjective
The adjectives which show that which and what thing is meant are called demonstrative adjectives.
Examples
This, that, these, those etc.
Difference between demonstrative pronouns and demonstrative adjectives
If this, that, those give an indication of some nouns, they are called demonstrative pronouns.
In order to better understand the difference between demonstrative pronouns and demonstrative adjectives, some sentences are explained in the given table.
| Demonstrative Pronouns | Demonstrative Adjectives |
| This is my pen. | This pen is mine. |
| This is a chair. | That chair is fine. |
| These are my candles. | These candles are mine. |
| Those are hills. | Those hills are high. |
10 – Indefinite Adjectives
Indefinite adjectives are those adjectives which point out the nouns. They often tell “how many” or “how much” of something.
Indefinite adjectives list
- All
- any
- another
- both
- each
- either
- few
- more
- many
- must
- several
- some
Examples
Use of indefinite adjectives in sentences
- There is little water in the jug.
- Many students are present in the classroom.
- Either of student can get scholarship.
- Several grocery items were present in store.
11 – Interrogative Adjective
The adjectives which are used with nouns to ask questions are called interrogative adjectives.
Examples
- Which book
- What time
- Whose car
Use of interrogative adjective in sentences
- Whose pen is this?
- Which way do you go?
- What time you will reach?
- Which book you like most?
- Whose case is this?
12 – Adjective of Position
This adjective is either used on subject or object before noun. It can also be used as complement.
Examples
- I saw an old tree.
- He is wise.
- This tree is high.
- This wall is long.
- This car is wide.
13 – Distributive Adjective
These are the adjectives which refer to each one of a number are called distributive adjectives.
Examples
- Each of you will pay the tax.
- Everyone should do his duty.
- Each of us will appear in the exams.
- Each of you should help the poor.
Further Reading
- 8 Parts of Speech with Examples
- Parts of Speech Chart (Printable)
- Parts of Speech Posters (Free)
- Adjective Examples (50 Sentences)