27 Figures of Speech with Examples | Complete Guide
A figure of speech is a mode of creating a great effect in words. It is stylistic devices that bring clarity in writing, vividness in ideas and beauty in expression.
In order to express the words or phrases in a better way, we use figures of speech. It may be a simile, metaphor, personification, etc.
Figures of Speech with Examples
There are numerous figures of speech. The number may cross the hundred. However, we have discussed 27 figures of speech with examples. These are the most important types which oftenly used in a language.
View also: Figures of Speech Worksheet with Answers
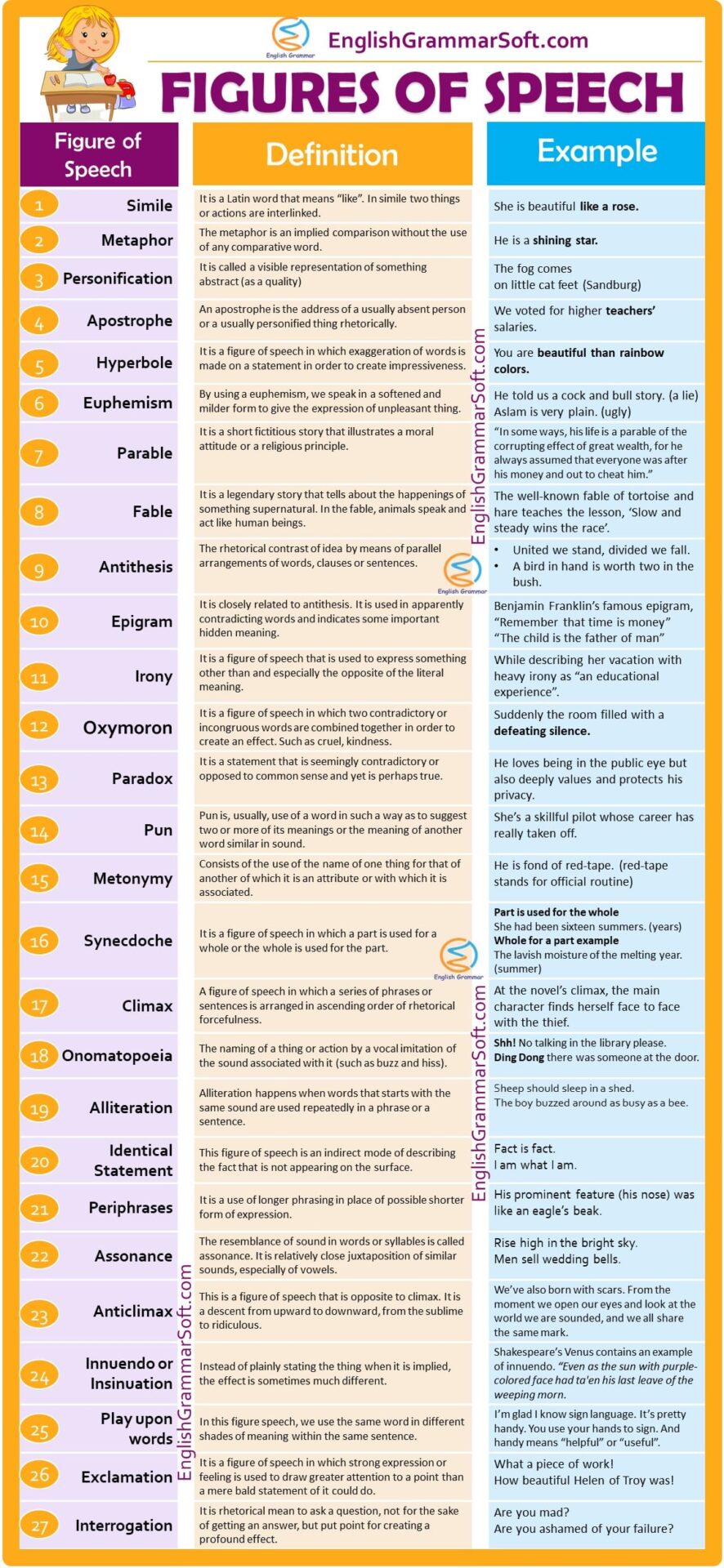
1 – Simile
It is a Latin word that means “like”. In simile two things or actions are interlinked.
Example: She is beautiful like a rose.
There are two types of similes.
- Simple
- Developed
1.1 – Simple Simile
It is expressed in a short and brief way.
Simple simile examples
- He wandered lonely as a cloud.
- The news spread like a fire.
- Rustam is strong like a mountain
1.2 – Developed Simile
It is the imitation of words that is expressed in a descriptive manner. Normally, it is used in epics.
Like some young cypress, tall and dark, and straight.
Which in a queen’s secluded garden throws
Its slight dark shadow on the moonlit turf,
By midnight, to a bubbling fountain’s sound
So slender sohrab seemed, so softly reared.
2 – Metaphor
The metaphor is an implied comparison without the use of any comparative word. In metaphor, words “like, so, as” are not used. For example,
He is like a Tarzan. (simile)
He is a Tarzan. (metaphor)
In the above example, we do not use the word “like” in metaphor.
Examples of Metaphor
- He is a shining star.
- She is facing black days of her life.
Further Reading:
3 – Personification
It can make things easier to imagine when you read them.
Personification is the representation of personal qualities or human feelings or motives to inanimate natural elements.
In short, it is called a visible representation of something abstract (as a quality)
It’s spring.
and the garden is changing its clothes,
putting away
its dark winter suits (Foster)
The fog comes
on little cat feet (Sandburg)
4 – Apostrophe
An apostrophe is the address of a usually absent person or a usually personified thing rhetorically.
In this figure of speech, a mark used to indicate the omission of letters or figures, the possessive case (as in “Maria’s book”), or the plural of letters or figures (as in “the 1970’s”).
Examples of Apostrophe
- We voted for higher teachers’ salaries.
- The court order required both parents’ consent.
5 – Hyperbole
Hyperbole is a figure of speech in which exaggeration of words is made on a statement in order to create impressiveness. It is an effective mode of securing attention, expression of emotion, and creating a poetic effect.
Hyperbole Examples
- You are beautiful than rainbow colors.
- That man is as tall as the camel.
- Your skin is softer than silk.
6 – Euphemism
By using a euphemism, we speak in a softened and milder form to give the expression of unpleasant thing. It is an indirect representation of a direct one so to avoid abruptness.
Euphemism Examples
- He told us a cock and bull story. (a lie)
- Aslam is very plain. (ugly)
- He was gathered to his forefathers. (he died)
7 – Parable
It is a short fictitious story that illustrates a moral attitude or a religious principle.
Example
“In some ways, his life is a parable of the corrupting effect of great wealth, for he always assumed that everyone was after his money and out to cheat him.”
8 – Fable
It is a legendary story that tells about the happenings of something supernatural. In the fable, animals speak and act like human beings. The well-known fable of tortoise and hare teaches the lesson, ‘Slow and steady wins the race’.
Example
The fable of the old man, his son, and the ass show the folly of attempting to please everyone.
The story he won the battle single-handedly is merely a fable.
9 – Antithesis
The rhetorical contrast of idea by means of parallel arrangements of words, clauses, or sentences. In antithesis, words or ideas are brought into contrast in order to create a balanced one against the other.
Examples
- United we stand, divided we fall.
- Man proposes, God disposes.
- A bird in hand is worth two in the bush.
10 – Epigram
It is closely related to antithesis. It is used in apparently contradicting words and indicates some important hidden meaning. The language of the epigram is remarkable for its brevity.
Example
Benjamin Franklin’s famous epigram,
“Remember that time is money”
“The child is the father of man”
11 – Irony
It is a figure of speech that is used to express something other than and especially the opposite of the literal meaning.
In other words, a usually humorous literally style or form is characterized by irony.
Examples
- “No doubt you are the people, and wisdom should die with you.”
- While describing her vacation with heavy irony as “an educational experience”.
- It was a tragic irony that he made himself sick by worrying so much about his health.
12 – Oxymoron
Oxymoron is a figure of speech in which two contradictory or incongruous words are combined together in order to create an effect. Such as cruel, kindness. It is a rhetorical device that can be used in order to reveal a paradox by using two self-contradictory terms.
- Suddenly the room filled with a defeating silence.
- Her singing was enough to raise the living dead.
- The sermon lasted for an endless hour.
- Stop being a big baby.
13 – Paradox
It is a statement that is seemingly contradictory or opposed to common sense and yet is perhaps true. The paradox is a rhetorical device used to attract attention, to secure emphasis.
Examples
- He loves being in the public eye but also deeply values and protects his privacy.
- Failures are the pillars of success.
- Cowards die many times before their death.
14 – Pun
Pun is, usually, use of a word in such a way as to suggest two or more of its meanings or the meaning of another word similar in sound.
Examples
- Firefighting sparks my interest.
- She’s a skillful pilot whose career has really taken off.
- He kept his spirits up by pouring spirits down.
15 – Metonymy
A figure of speech consists of the use of the name of one thing for that of another of which it is an attribute or with which it is associated (such as “crown” in “lands belonging to the crown”.)
Metonymy examples are;
- He is fond of red-tape. (red-tape stands for official routine)
- The bench of judges.
- He addressed the chair. (chairman)
- A smooth tongue (pleasant speech) wins favor.
16 – Synecdoche
Synecdoche is a figure of speech in which a part is used for a whole or the whole is used for the part.
Examples
A part is used for the whole,
- Fifty sail for fifty ships.
- She had been sixteen summers. (years)
- They left their father’s roof. (home)
Whole for a part example,
- Society for high society.
- The lavish moisture of the melting year. (summer)
- A foeman worthy of his steel. (sword)
- The canvas (oil painting) glows.
17 – Climax
A figure of speech in which a series of phrases or sentences is arranged in ascending order of rhetorical forcefulness.
The climax is the highest point of interest in narrative fiction. In other words, it is the point of highest dramatic tension or a major turning point in the action (as of a play).
- The movie’s climax is a fantastic chase scene.
- At the novel’s climax, the main character finds herself face to face with the thief.
- The protest in May was the climax of a series of demonstrations in the nation’s capital.
18 – Onomatopoeia
The naming of a thing or action by a vocal imitation of the sound associated with it (such as buzz and hiss).
- Shh! No talking in the library please.
- Ding Dong there was someone at the door.
- Ouch! You just stepped on my toe.
- Ahem! I can hear everything you are saying about me.
19 – Alliteration
It is the repetition of one or more similar consonants in successive words. In other words, alliteration happens when words that starts with the same sound are used repeatedly in a phrase or a sentence.
- Sheep should sleep in a shed.
- The boy buzzed around as busy as a bee.
- Go and gather the green leaves on the grass.
- I saw a saw that could cut any other saw I ever saw.
20 – Identical Statement
This figure of speech is an indirect mode of describing the fact that is not appearing on the surface.
Examples
- Fact is fact.
- I am what I am.
- Do whatever you want to do.
- Sensation is sensation.
21 – Periphrases
It is a use of longer phrasing in place of a possible shorter form of expression. The definition of periphrases is very similar to that of circumlocution, which also means talking around something by adding more words.
It is a single word that can express a great multitude of complexity by itself.
- The viewless couriers of the air. (winds)
- His prominent feature (his nose) was like an eagle’s beak.
- He resembled the animals that browses on thistles. (an ass)
22 – Assonance
The resemblance of sound in words or syllables is called assonance. It is a relatively close juxtaposition of similar sounds, especially of vowels.
- Rise high in the bright sky.
- The rain in Spain falls mainly on the plain.
- Men sell wedding bells.
23 – Anticlimax
This is a figure of speech that is opposite to climax. It is a descent from upward to downward, from the sublime to ridiculous. It is usually a sudden transition in discourse from a significant idea to a trivial or ludicrous idea.
Example
- We’ve also born with scars. From the moment we open our eyes and look at the world we are sounded, and we all share the same mark.
24 – Innuendo or Insinuation
Instead of plainly stating the thing when it is implied, the effect is sometimes much different. It is called innuendo. It is a veiled or equivocal reflection on character or reputation.
- Robert Frost’s entire poem “Putting in the seed” is one long innuendo that can also be considered a conceit. Frost uses suggestive words and images like “smooth bean and wrinkled pea”.
- Shakespeare’s Venus contains an example of innuendo. “Even as the sun with purple-colored face had ta’en his last leave of the weeping morn.
25 – Play upon words
In this figure speech, we use the same word in different shades of meaning within the same sentence. It is pun or joke made using a word or phrase which has double meaning.
Example
- I’m glad I know sign language. It’s pretty handy. You use your hands to sign. And handy means “helpful” or “useful”.
26 – Exclamation
Exclamation is a figure of speech in which a strong expression or feeling is used to draw greater attention to a point than a mere bald statement of it could do.
Example
- What a piece of work!
- How beautiful Helen of Troy was!
27 – Interrogation
Interrogation is a rhetorical means to ask a question, not for the sake of getting an answer, but put point for creating a profound effect.
Example
- Are you mad?
- Are you ashamed of your failure?
- Can you imagine that?
You may also like:
Download: Figures of Speech with examples pdf
Literary Devices








This article details so much more info than similar blogs, and it’s incredibly helpful to me. Will follow you to see more writing from you! is it okay to share this?
Thank you Sunny. For sure, you can share it.
I read through this and found it useful.
Amazing content is provided with good explanation and examples. It helps me a lot .I see forward for more writing content.
Good word ????????????
Very understanding please send me links of exercise
Am really impressed in it.
I love it. Thank-you
It’s hard to find educated people for this topic, however, you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks