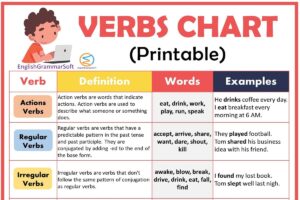
Intransitive Verbs with Examples
Intransitive verb does not take a direct object. That is, the action does not transfer to someone or something. You cannot “direct” the action of an intransitive verb. For example,
These sentences do not have any object.
- The snow fell gently overnight.
- I laughed out loud.
- They arrived at 3:00 p.m.
- The lamp went out.
- He slept soundly.
What are intransitive verbs?
An intransitive verb is a verb that does not take an object. This means that the action of the verb happens without anyone or anything else being involved.
Examples
- I laughed.
- He slept.
- The baby cried.
Sometimes we can use an intransitive verb with a prepositional phrase: We arrived at the party at eight o’clock. In this sentence, arrived is still an intransitive verb because it does not take an object. The prepositional phrase at the party tells us where we arrived.
We cannot use arrived with a direct object: We arrived them at the party at eight o’clock. This sentence is incorrect because arrived takes no object.
Intransitive Verbs List
Some common intransitive verbs are listed below. This is by no means a complete list, but it will give you a good idea of the types of verbs that are intransitive.
Action Verb
- arrive
- come
- cry
- depart
- fall
- go
- grow
- jump
- make
- occur
- rise
- run
- sleep
- teach
Mental State Verbs
- believe
- doubt
- feel
- know
- forget
- remember
- think
Sensory Experience Verbs
- see
- hear
- feel
- smell
- taste
Emotion Verbs
- love
- excite
- depress
- hate
- prefer
The difference between transitive and intransitive verbs
A transitive verb is an action verb that expresses a direct relation between the subject and the object. The subject is the actor and the object is the target of the action. For example, in the sentence “I baked a cake.” “I” is the subject, “baked” is the verb and “cake” is the object. You can see that there is a clear connection between the subject and object.
An intransitive verb does not have a direct object. It expresses either no relation between subject and object or only an indirect relation. In other words, with intransitive verbs, you can’t answer the question “What did X do?” following the verb. For example, in the sentence “He ran quickly,” there is no direct relation between “He” and anything else in terms of action. You can ask “What did he do?” but you cannot answer this question with a direct object. Compare this to the previous sentence with a transitive verb: “He baked a cake.” Here you can answer the question “What did he bake?” with “Cake.”
How to use intransitive verbs
There is not a noun that follows an intransitive verb to receive the action of the verb. The verb always acts on the subject of the sentence. You can usually tell if a verb is intransitive if it uses the object indirectly or does not use at all.
Examples:
- Later today we will leave.
- After dinner we will study.
- We will leave later today .
- We will study after dinner .
Examples of intransitive verbs
Here are some examples of intransitive verbs:
- I am happy today.
- I breathed a sigh of relief when all my exams were over.
- The fire burned brightly all night long, until it was put out by the fire department.
- The man walked down the street.
- The dog is running around outside.
- Tom’s father died a month ago.
- The product your are searching for does not exist.
- He tried but failed.
- She laughed loudly.
- I like to eat popcorn while I watch TV.
- This plant has grown two feet in the last month!
- The baby sleeps all day.
- The plane flew over the building.
- It is raining outside.
- He walked away angrily after the argument.
- The tree fell over in the storm.
- The boat sank.
- The sun set behind the clouds.
- I slept soundly.
- She is tall.
- She gets up at 8 o’clock every morning.
- She was excited about her new job
Common mistakes with intransitive verbs
One common mistake with intransitive verbs is using them transitively. An intransitive verb cannot take an object; it is only used to describe an action that affects the subject. For example, the verb “sleep” is intransitive and can only be used to describe what the subject (e.g., I, you, he, she, it) is doing; it cannot take an object (e.g., *I sleep the baby).
Other mistakes with intransitive verbs include:
- Using an object pronoun when a subject pronoun is needed:
- She sleeps her two hours every day.
- She sleeps two hours every day.
- Leaving out the pronoun altogether:
- Sleeping soundly, the baby didn’t hear mother leave for work.
- Sleeping soundly, the baby didn’t hear her mother leave for work.
Some verbs can be used both ways, with or without a direct object. When used without a direct object, these verbs are usually intransitive.
These verbs can be followed by an adjective, adverb, or prepositional phrase, but not a direct object. For example:
- arrive
- leave
- remain
- sleep
- sit
- stand
For example:
- The plane arrived late. (adverb)
- The plane arrived at the airport. (prepositional phrase)

More to read