Four Modes of Discourse
What is discourse?
Discourse can be described as the exchange and circulation of ideas amongst those who have different views or opinions, regardless of their social standing. It can also be viewed as a form of written or spoken communication which aims to persuade others to accept or promote one’s point of view.
At its core, discourse is all about dialogue and persuasion. Because it is an online form of communication, discourse is inherently unstable and subject to rapid change, both internally within a community and outside of it as well.
Discourse is not purely a matter of words spoken on the street. These are collected and organized, such as in Blog Discourse is a text created for the sole purpose of sharing opinions or ideas. Forum and message boards in other online spaces such as message boards on Facebook or Twitter are also discourse hubs. When posting messages, topics are often discussed and questions are often posed. In short, Discourse is anything that relates to words and ideas.
Discourse is the product of interaction. Language is the most immediate and obvious example, but it can also be found in art, politics, entertainment, and even software development. As such, discourse provides us with a look into the minds of those who take part in these forms of communication. Language, like everything else, has its own inherent context, meaning, and value that becomes revealed through its interaction with other different things. This is why it is important to understand the context of any discourse you read or hear.
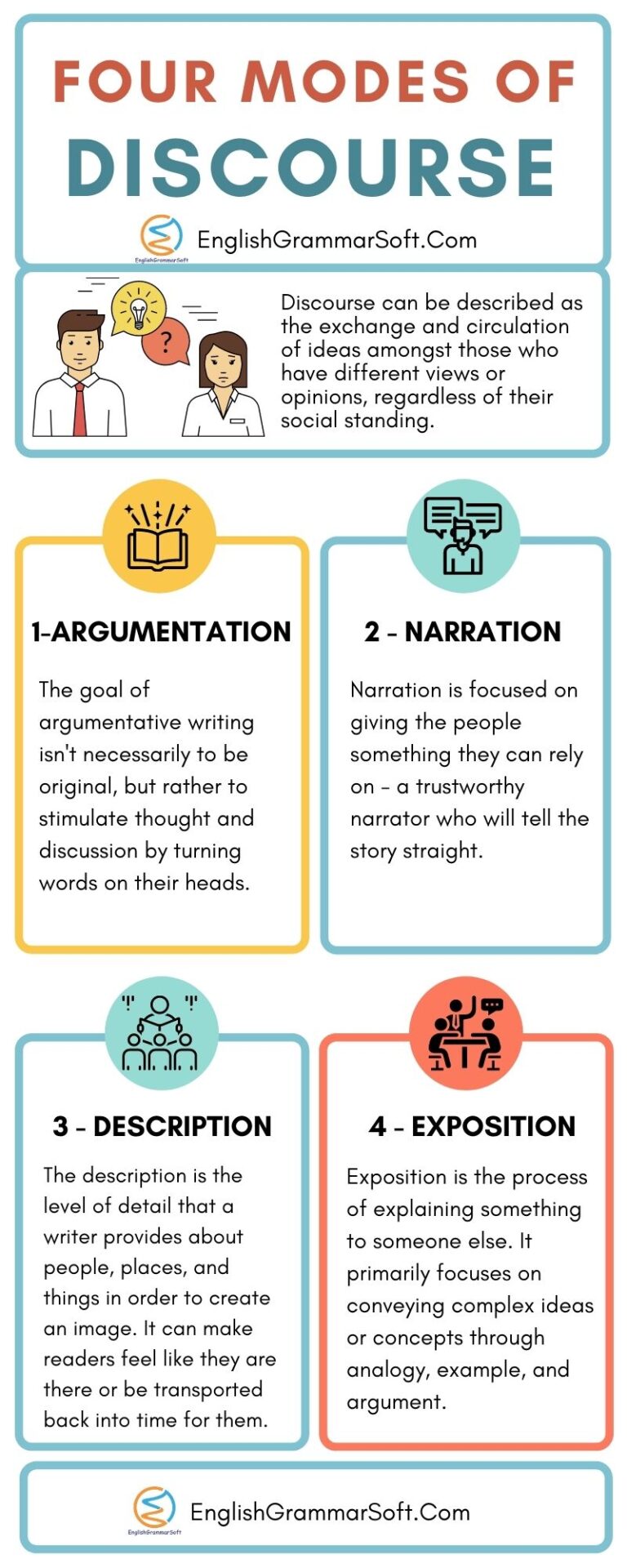
Four Modes of Discourse
1 – Argumentation
At its base, argumentative writing is about communicating an argument using words. The goal of argumentative writing isn’t necessarily to be original, but rather to stimulate thought and discussion by turning words on their heads. While there are many different ways one can engage in argumentative writing, it varies based on the type of discourse being conducted.
Argumentative writing appeals to your emotions while persuasive writing uses logic and facts to showcase a point. Both consist of descriptive sentences designed to grab attention and interest readers, but there is a key difference: persuasive writing is about making you decide (after reading), while argumentative writing aims to get your reader to agree with you.
2 – Narration
Narration is focused on giving the people something they can rely on – a trustworthy narrator who will tell the story straight. This type of discourse relies heavily on communication skills and developing relationships with other people (as well as an understanding of how their actions fit into the larger narrative).
In every story, there is a character who tells the story, and it is always the job of the narrator to add color, drama, anxiety, or humor to what is being said. Voice actors have a particular skill in this area because they can imbue any personality into their monologues. You might think that storytellers only focus on dramatic figures like politicians and celebrities, but that couldn’t be further from the truth. Aside from being able to tell stories, audiobook narrators have other skills: being emotionally stable enough to do it.
Narration is usually delivered through a dramatic or musical performance where an experienced narrator paints a dramatic picture based on exchanged words and a story or anecdote. Accounts vary on whether the narration is performed by an individual or an institutional voice such as a newspaper article or a professor’s lectures. Stage play narrators vary on their authority; some are employed as professionals while others may be employed.
3 – Description
The description is the level of detail that a writer provides about people, places, and things in order to create an image. It can make readers feel like they are there or be transported back into time for them.
The primary sense of discourse is the five basic human senses: sight, sound, smell, touch, and taste. People use descriptions to communicate effectively and efficiently with one another. In a largely literate culture such as ours, having a sense of discourse is essential for finding common ground with others. It helps us work together effectively by identifying common interests or styles of thinking that we can borrow from others.
4 – Exposition
Exposition, definition, and problem-and-solution are the three things that will make your audience engage with you. Explain something complex in simple terms so that people can easily grasp the main idea. Use examples to make your points more clear and present. When you need to stand out in a crowd, always use exclamatory phrases or fun words that draw attention to something interesting you’ve done. You should always strive to communicate something clearly and concisely so your audience can understand it fully without your having to elaborate.
Exposition can be used in three ways.
- First, it can present information in a way that an inexperienced reader will be able to understand and absorb.
- Second, it can provide background information which will probably be familiar to someone in the audience.
- And third, it can connect the audience with an expert who can help provide clarity.
Exposition is the process of explaining something to someone else. It primarily focuses on conveying complex ideas or concepts through analogy, example, and argument. In education, for example, teachers might want to explain concepts of learning in a way that makes students interested in the material. In business, executives might want to communicate a plan to the employees in order to enhance their productivity.
Further Reading
- Examples of Assonance
- Examples of Innuendo
- Examples of Exclamation in Literature
- Onomatopoeia Examples
- Interrogation Examples in Literature
- Types of Paradox in Literature
- Oxymoron Examples from Literature
- Synecdoche Examples in Literature
- Figures of Speech with Examples
- Antithesis Examples in Literature
- Euphemism Figure of Speech
- Pun Figure of Speech
- Metonymy Classification & Examples
- What is a simile in literature? How to write a good simile?
- Types of Metaphor with Examples
- Apostrophe as a Figure of Speech
- Personification with Examples
- Hyperbole Definition and Examples
- Fable Meaning and Examples in Literature
- What is Epigram in Figure of Speech?