Free Printable Verb Chart
This printable verb chart is designed to help students learn and review the most common verbs in the English language.
What are verbs?
Verbs are words that express action or state of being. They’re the most important part of speech because they drive the sentence. Verbs are of different types.
Verbs are also classified based on what they do to their subjects. Some verbs act as linking verbs and connect the subject with additional information about it (he is tall). Others act as action verbs, which indicate some sort of action or state of being (he runs quickly).
What are the 10 types of verbs?
In this table we have summarized 10 types of verbs.
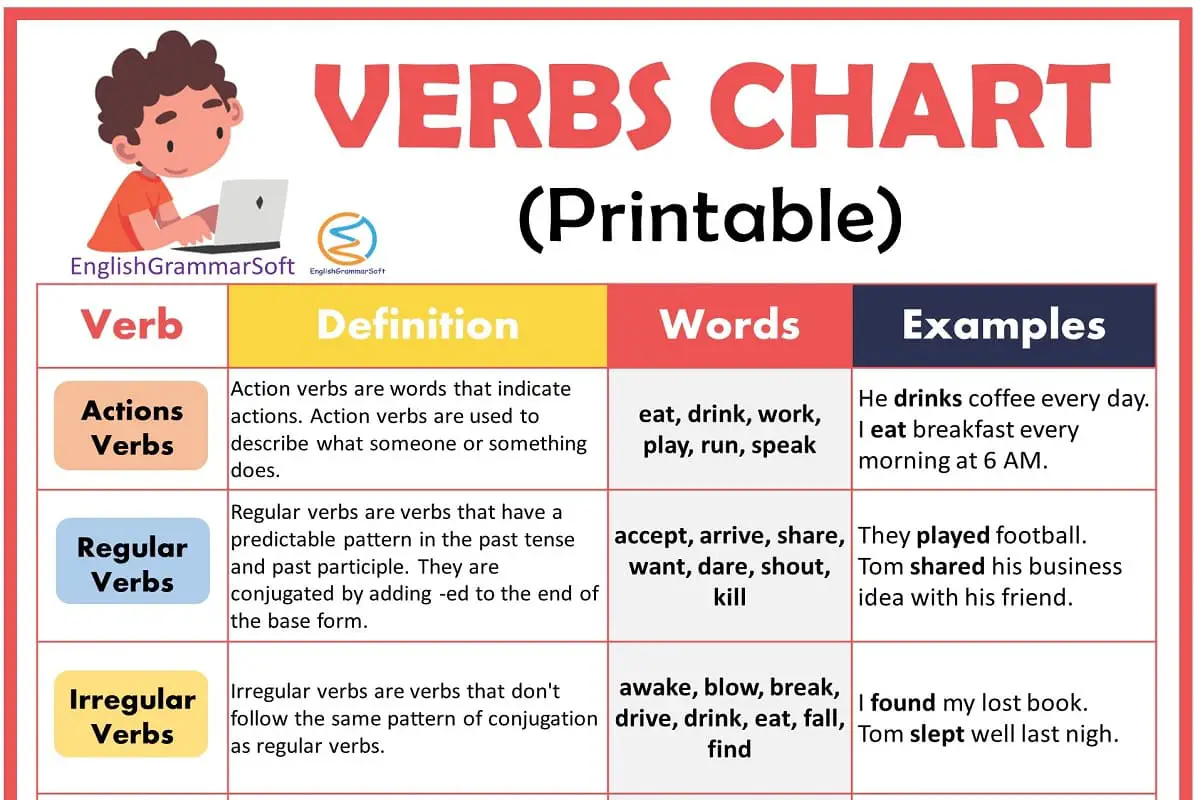
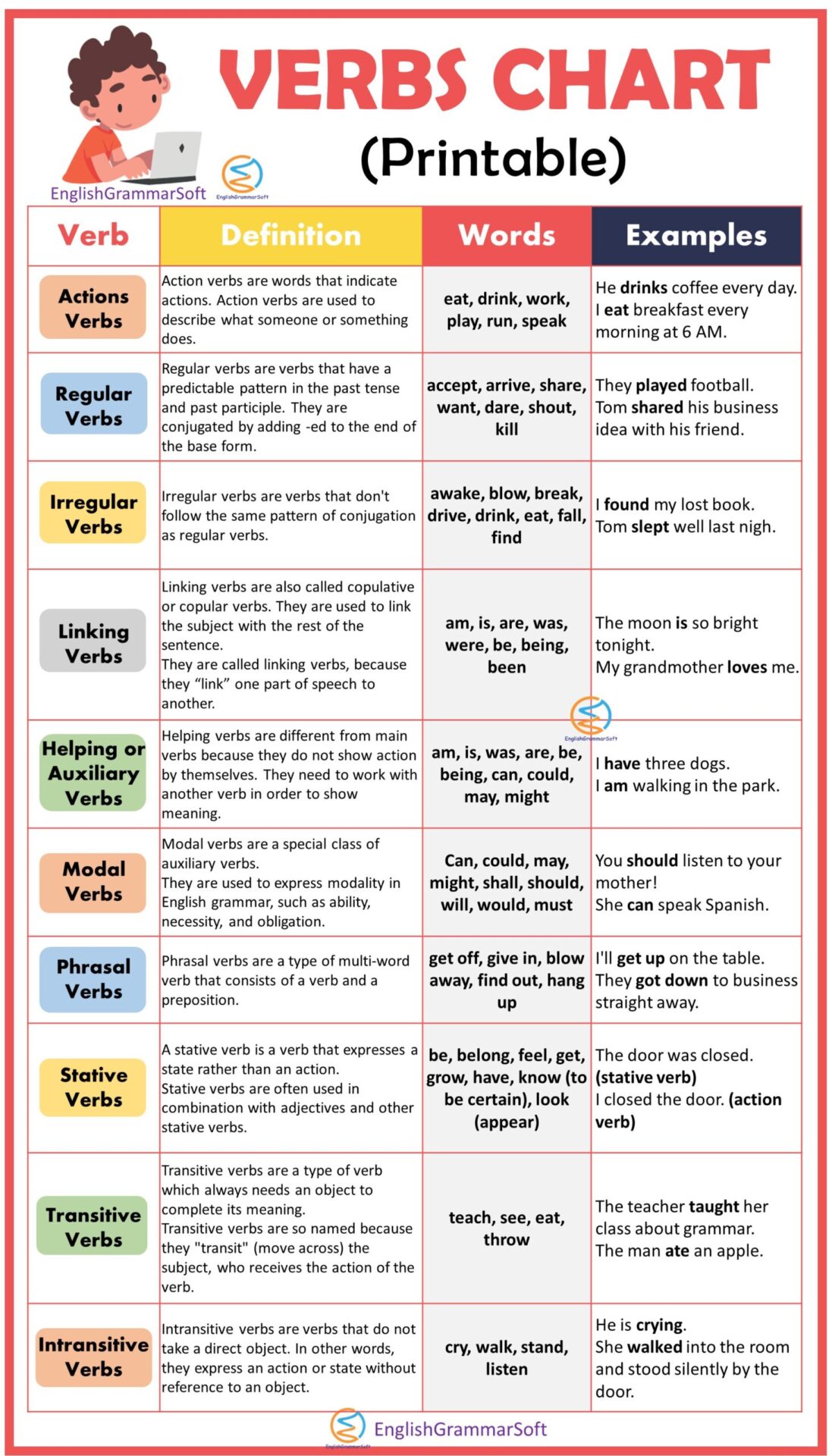
| Verb | Definition | Words | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actions Verbs | Action verbs are words that indicate actions. Action verbs are used to describe what someone or something does | eat, drink, work, play, run, speak | He drinks coffee every day. I eat breakfast every morning at 6 AM. |
| Regular Verbs | Regular verbs are verbs that have a predictable pattern in the past tense and past participle. They are conjugated by adding -ed to the end of the base form. | accept, arrive, share, want, dare, shout, kill | They played football. Tom shared his business idea with his friend. |
| Irregular Verbs | Irregular verbs are verbs that don’t follow the same pattern of conjugation as regular verbs. | awake, blow, break, drive, drink, eat, fall, find | I found my lost book. Tom slept well last nigh. |
| Linking Verbs | Linking verbs are also called copulative or copular verbs. They are used to link the subject with the rest of the sentence. They are called linking verbs, because they “link” one part of speech to another. | am, is, are, was, were, be, being, been | The moon is so bright tonight. My grandmother loves me. |
| Helping Verbs or Auxiliary Verbs | Helping verbs are different from main verbs because they do not show action by themselves. They need to work with another verb in order to show meaning. | am, is, was, are, be, being, can, could, may, might | I have three dogs. I am walking in the park. |
| Modal Verbs | Modal verbs are a special class of auxiliary verbs. They are used to express modality in English grammar, such as ability, necessity, and obligation. | Can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, must | You should listen to your mother! She can speak Spanish. |
| Phrasal Verbs | Phrasal verbs are a type of multi-word verb that consists of a verb and a preposition. | get off, give in, blow away, find out, hang up | I’ll get up on the table. They got down to business straight away. |
| Stative Verbs | A stative verb is a verb that expresses a state rather than an action. Stative verbs are often used in combination with adjectives and other stative verbs. | be, belong, feel, get, grow, have, know (to be certain), look (appear) | The door was closed. (stative verb) I closed the door. (action verb) |
| Transitive Verbs | Transitive verbs are a type of verb which always needs an object to complete its meaning. Transitive verbs are so named because they “transit” (move across) the subject, who receives the action of the verb. | teach, see, eat, throw | The teacher taught her class about grammar. The man ate an apple. |
| Intransitive Verbs | Intransitive verbs are verbs that do not take a direct object. In other words, they express an action or state without reference to an object. | cry, walk, stand, listen | He is crying. She walked into the room and stood silently by the door. |
Printable Verb Chart
- MORE TO DOWNLOAD
- Parts of Speech Chart
- Parts of Speech Posters
- Printable Nouns Chart
- Printable Pronouns Chart
- Printable Adjective Chart
- Printable Adverb Chart
- Printable Preposition Chart
More to read