What are the 4 types of conjunctions? | Conjunction rules with examples
Conjunction is a word that is used to connect clauses, words, or phrases. It is important for clarity and understanding in writing.
Conjunction List
He is the list of most commonly used conjunction words.
- and
- because
- either
- however
- lest
- only
- till
- unless
- so
- as well as
- as if
- but
- else
- if
- or
- still
- too
- until
- either – or
- neither – nor
- so – as
What are the 4 types of conjunctions?
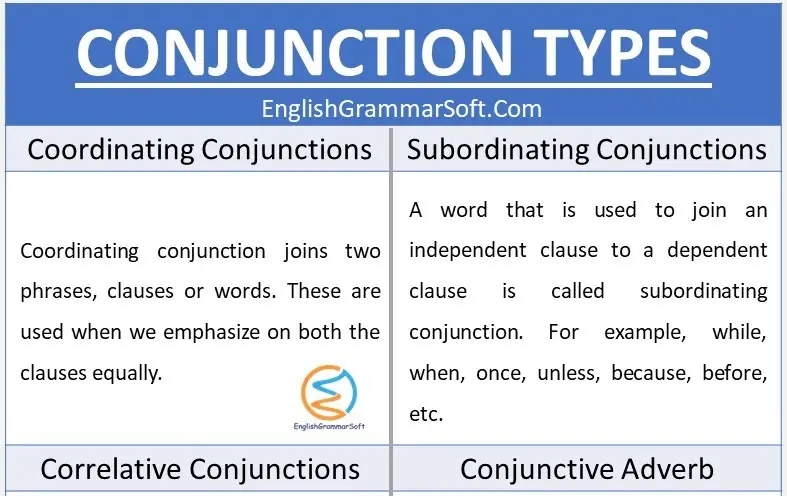
i – Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunction joins two phrases, clauses or words. These are used when we emphasize on both the clauses equally.
There are seven coordinating conjunctions:
- and
- but
- for
- nor
- or
- so
- yet
Examples
- Would you like to take tea or juice?
- I hate to solve equations, for these are difficult to solve.
ii – Subordinating Conjunctions
A word that is used to join an independent clause to a dependent clause is called subordinating conjunction. For example, while, when, once, unless, because, before, etc.
A dependent clause can add value to an independent clause. When we connect the dependent clause to an independent clause, it becomes more meaningful and has more information.
- He was eating chips when he was watching TV.
- He got the first position in the exam because he worked hard.
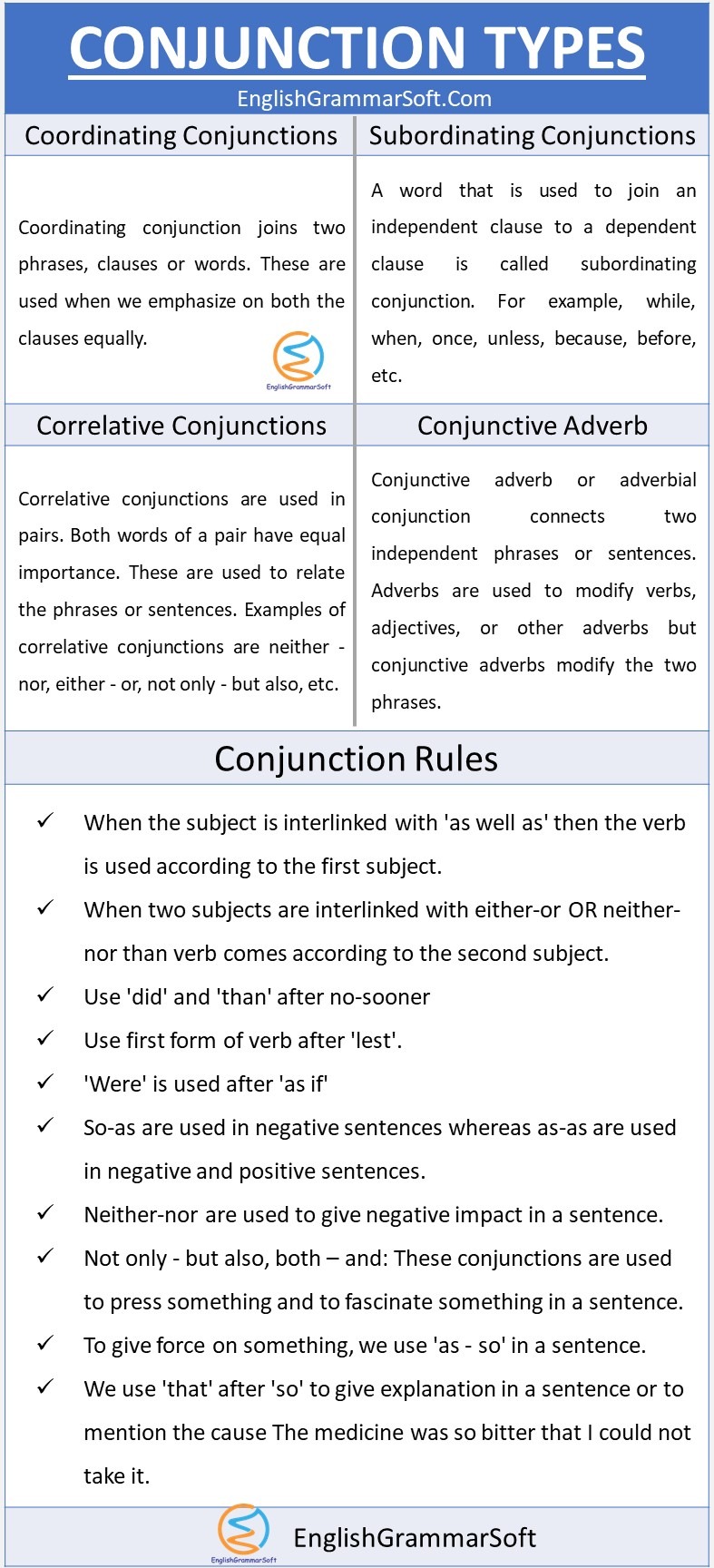
iii – Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions are used in pairs. Both words of a pair have equal importance. These are used to relate the phrases or sentences. Examples of correlative conjunctions are neither – nor, either – or, not only – but also, etc.
- He can go to either beach or a park to spend his holiday.
- Neither Jimmy nor Tom attended the party.
iv – Conjunctive Adverb
Conjunctive adverb or adverbial conjunction connects two independent phrases or sentences. Adverbs are used to modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs but conjunctive adverbs modify the two phrases.
Some conjunctive adverbs are likewise, again, similarly, in addition etc.
Examples
- I wanted to go to a park; however, my friend wanted to see a movie.
- My job description is very tough; on the other hand, I really enjoy the facilities offered to me.
Conjunction rules with examples
When the subject is interlinked with ‘as well as’ then the verb is used according to the first subject.
Examples
- He as well as I is at fault.
- I as well he am at fault.
When two subjects are interlinked with either-or OR neither-nor than verb comes according to the second subject.
Examples
- Either I or you are going to the park.
- Either you or I am going to the park.
- Neither you nor I am a teacher.
- Neither I nor you are a hunter.
Use ‘did’ and ‘than’ after no-sooner
Example
- No sooner did the teacher enter the class room than the boys stood up.
Do not use ‘not’ when ‘unless’ is present in the sentence.
- Unless you work hard, you cannot pass.
Use first form of verb after ‘lest’.
- Be careful lest you should lose everything.
‘Were’ is used after ‘as if’
Examples
- He looks as if he were weary.
- She talks as if she were mad.
So – as
So-as are used in negative sentences whereas as-as are used in negative and positive sentences.
Examples
- He is as strong as you.
- He is not so strong as you.
Neither – nor
Neither-nor are used to give negative impact in a sentence.
Example
- Neither you nor your friend has stolen my watch.
Not only – but also, both – and
These conjunctions are used to press something and to fascinate something in a sentence.
Examples
- He is not only intelligent but also hard working.
- He is both poor and hard working.
As – So
To give force on something, we use ‘as – so’ in a sentence.
Example
- As you sow, so shall you reap.
So – that
We use ‘that’ after ‘so’ to give explanation in a sentence or to mention the cause which has some effect.
Example
- The medicine was so bitter that I could not take it.
Read also: 8 Parts of Speech with Examples
Further Reading